The How of Legal AI
Uwais Iqbal • 2022-11-03
AI is commonly confused with automation. AI can do automation but there is more that AI can offer.
AI is usually used to train a model to perform a specific task. This aspect is the What of Legal AI - what task the AI will perform e.g. to extract information or classify a document.
There is also another aspect concerning the approach. In other words, the How of Legal AI - how will AI be used to carry out the particular task at hand? It’s commonly understood that AI can be used to automate tasks. However, this is just one way of how AI can be used.
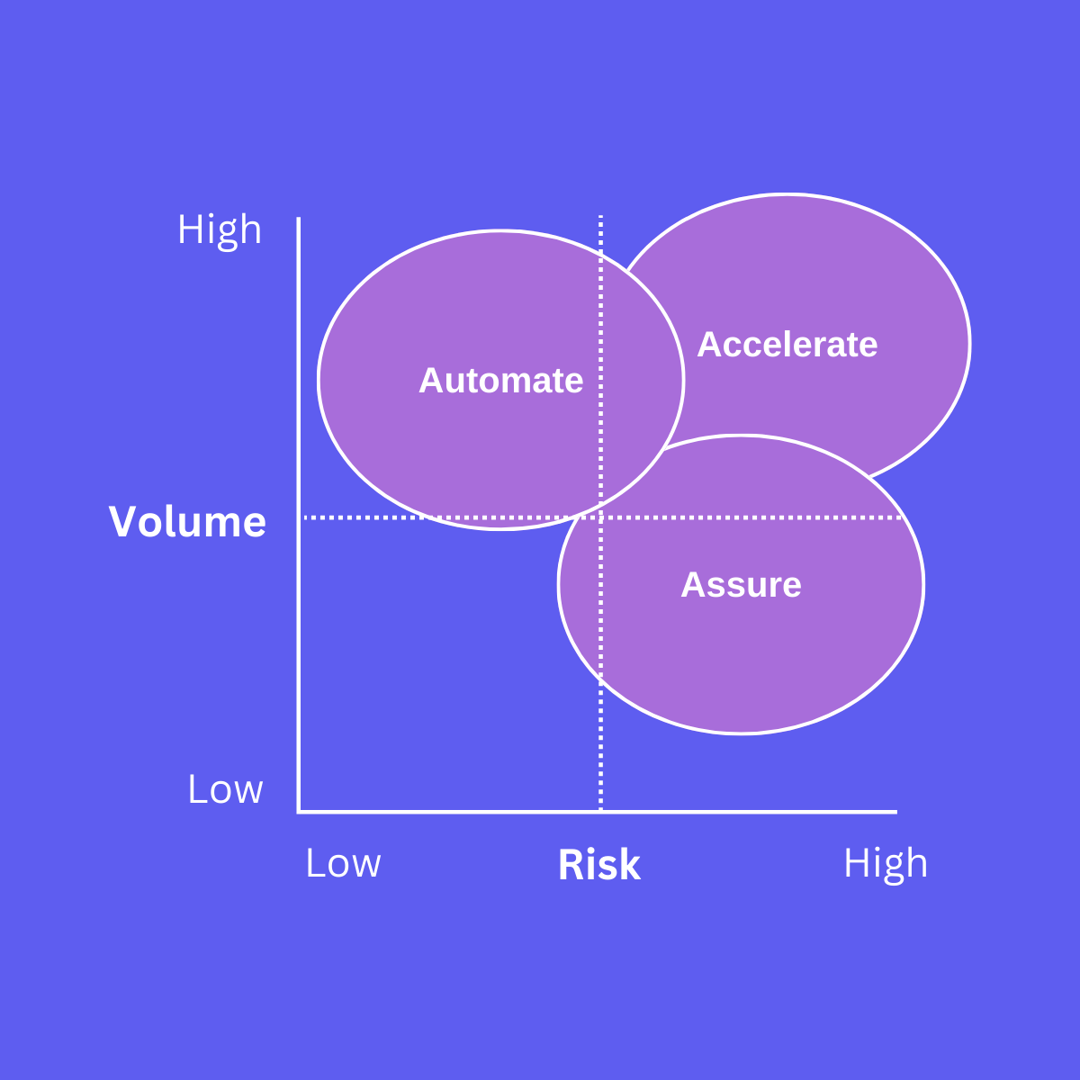
The Risk Volume Matrix
To understand the How of Legal AI we need to introduce two concepts:
- Volume – Given a particular task, volume captures the number of times the task is to be performed.
- Risk - Given a particular task, risk captures the potential cost of a mistake. This can either be in terms of financial cost or cost to reputation.
We can now put together a risk-volume matrix to understand the different approaches of AI. The risk/volume matrix is a framework for determining the How of Legal AI under different scenarios with respect to risk and volume.
The Hows of Legal AI
There are three different Hows of Legal AI:
- Automate
- Assure
- Accelerate
Getting clear on the How of Legal AI will inform the choice of model, the extent of user interaction as well as the data requirements for the AI model.
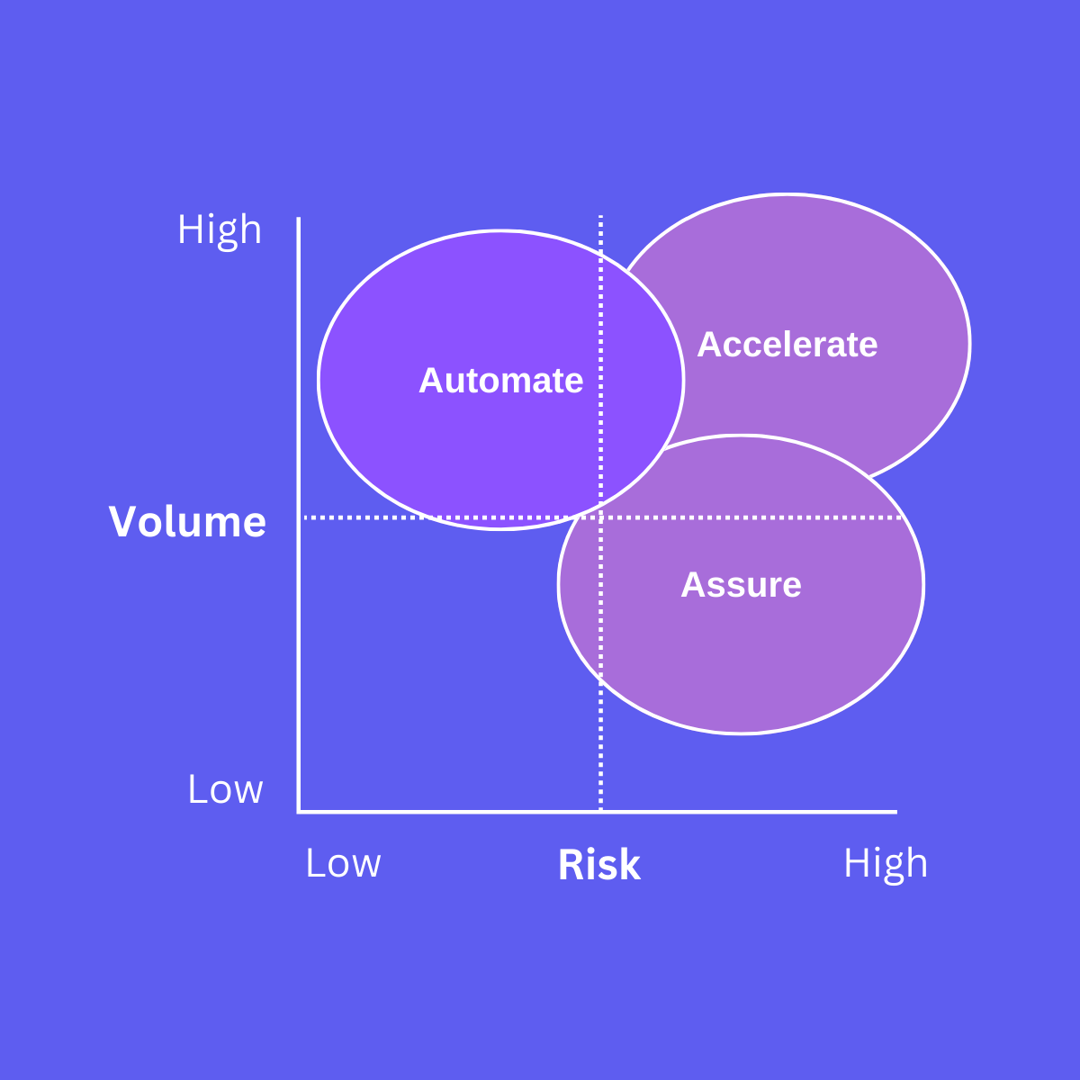
Automate
AI can be used in high-volume, low-risk scenarios to automate tasks and reduce human capital.
High volume means that AI can be leveraged to scale expertise in performing a particular task where otherwise vast resources of human capital would be needed. Low risk means that the penalty or cost of the AI making a mistake is very low. In such circumstances, AI can be trained to scale expertise for a particular task and automate the task thereby reducing the dependency on human capital.
A typical use case involves using AI to automate the extraction of fields from a set of contracts.
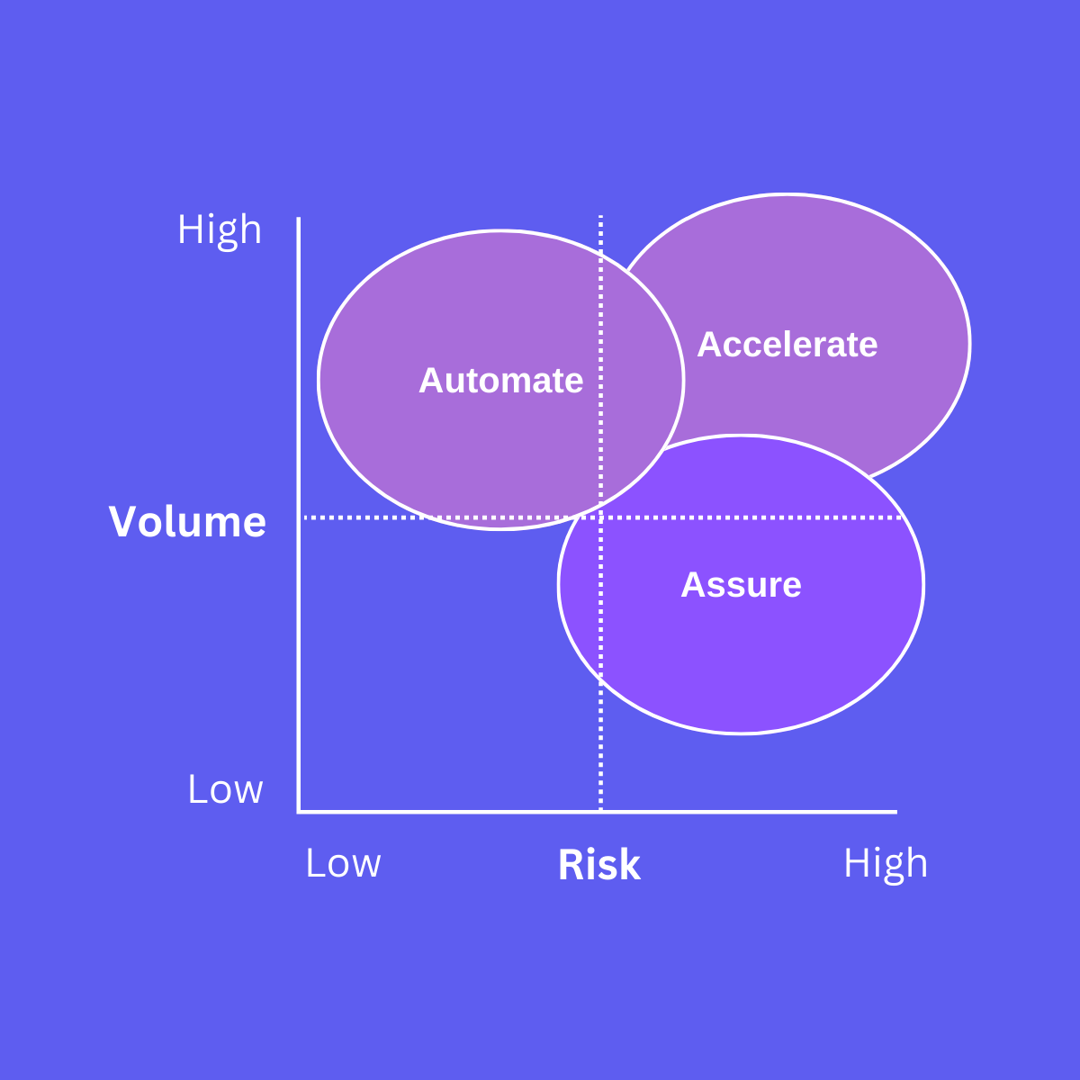
Assure
AI can be used in low-volume, high-risk scenarios to provide assurance in tasks and increase confidence. Low volume means that the human will always be relevant in such tasks. High risk means that making a mistake and getting things wrong is very costly. As a result, AI can play a role to support the human to provide assurance in such tasks.
A typical example involves conducting legal research. AI can be used to ensure that no relevant cases have been missed during legal research and help provide peace of mind that all bases have been covered.
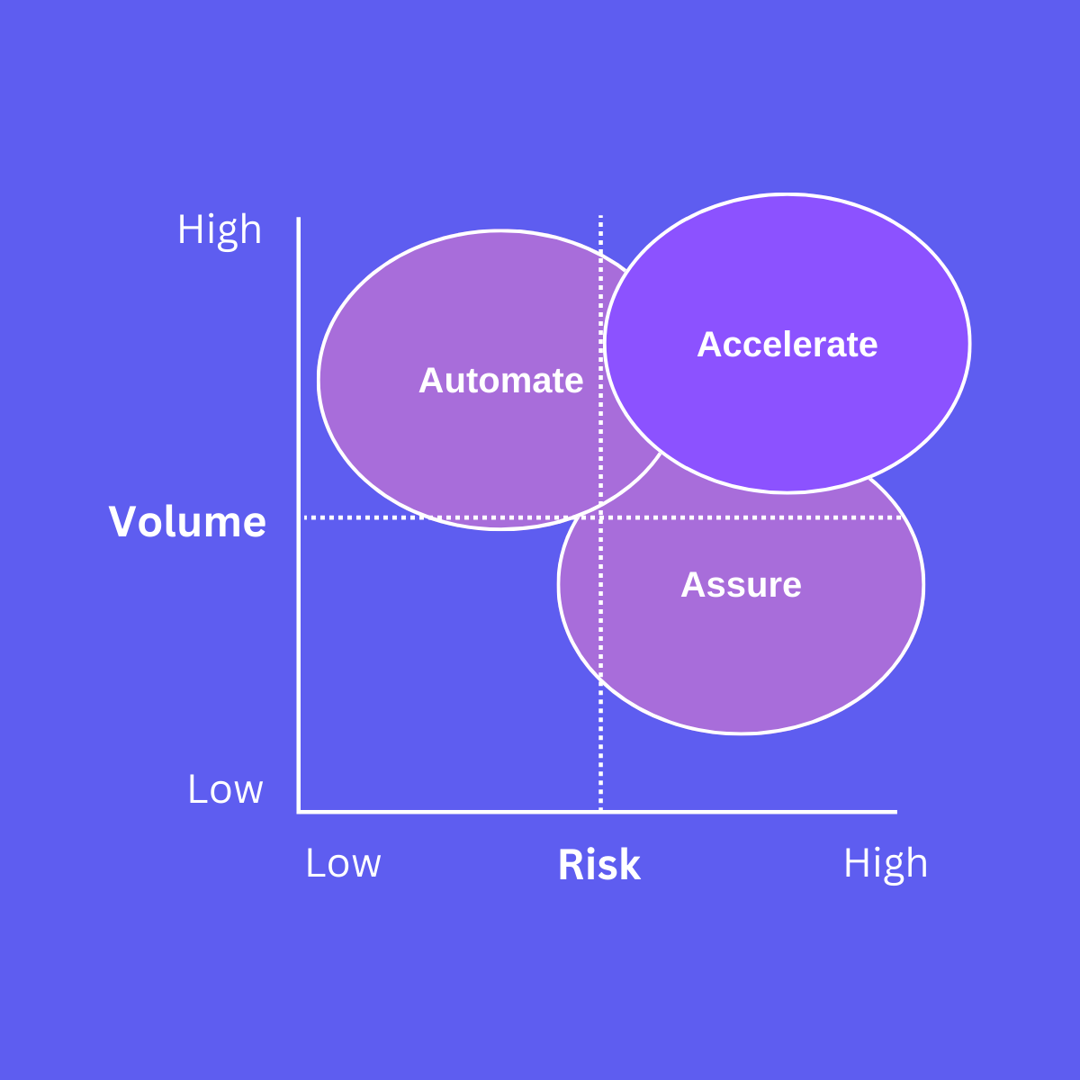
Accelerate
AI can be used in high-volume, high-risk scenarios to accelerate jobs and improve efficiency. High volume means that AI can be leveraged to scale expertise in performing a particular task where otherwise vast resources of human capital would be needed. High risk means that making a mistake and getting things wrong is very costly.
In such circumstances the human and machine work in collaboration to reach the desired objective in a shorter time span. AI plays a role to speed up the usual workflow of a legal professional creating efficiencies and completing tasks quicker.
A typical use case of acceleration is contract review. AI can be used to highlight and surface deviations in wording that may be risky to reduce the time it takes for a lawyer to review the contract and accelerate contract negotiations.
Applying the How of Legal AI
Once the What of Legal AI has been determined - what task the AI should perform, the How of Legal AI should be determined. A particular task e.g. extracting fields from a contract as part of contract review can be done in any of these ways. AI can be used to automate the extraction of fields from a contract where there is minimal human involvement. AI can be used to accelerate the extraction of fields from a contract where suggestions simply surfaced to the user. Or, AI can be used to provide assurance when extracting fields from a contract by checking through a completed review to check if anything has been missed.
Legal AI is more than just Automation
It’s a common fallacy to conflate AI with automation. It’s true that AI can be used to automate, but this is only in the particular case of a high-volume low-risk scenario. As we have seen, there are other scenarios where AI can play a role.
Understanding the How of Legal AI will help to resolve problems in implementing and adopting AI tools and solutions. If what you really need is an AI acceleration solution, an AI automation solution won’t be of much use.
Resources